Bootstrap Breakpoints Grid
Introduction
Accepting in idea all the feasible display screen sizes where our online pages could ultimately present it is essential to make up them in a method approving universal very clear and powerful visual appeal-- generally applying the support of a highly effective responsive system such as one of the most popular one-- the Bootstrap framework which most current edition is now 4 alpha 6. However, what it truly does to help the pages appear excellent on any sort of display screen-- why don't we have a look and notice.
The fundamental idea in Bootstrap typically is putting some structure in the endless possible device display screen sizes ( or else viewports) positioning them in a number of variations and styling/rearranging the web content properly. These are additionally named grid tiers or display dimensions and have developed quite a bit via the different editions of probably the most popular recently responsive framework around-- Bootstrap 4.
The way to apply the Bootstrap Breakpoints Grid:
Typically the media queries get determined with the following format @media ( ~screen size condition ~) ~ styling rules to get applied if the condition is met ~. The terms can limit one end of the interval like min-width: 768px of both of them like min-width: 768px - while the viewport size in within or else equivalent to the values in the conditions the rule uses. As media queries are component of the CSS language there certainly may be more than just one query for a single viewport width-- if so the one particular being really checked out with internet browser last has the word-- much like standard CSS rules.
Improvements of Bootstrap editions
In Bootstrap 4 unlike its forerunner there are actually 5 screen sizes yet since recent alpha 6 build-- only 4 media query groups-- we'll return to this in just a sec. Considering that you very likely realise a .row within bootstrap has column features maintaining the real page material that can surely extend up to 12/12's of the viewable width accessible-- this is oversimplifying yet it's another thing we are certainly speaking about here. Each and every column element get specified by just one of the column classes including .col - for column, display scale infixes defining down to which screen size the content will stay inline and will cover the whole horizontal width below and a number showing how many columns will the component span when in its display screen dimension or above.
Screen sizes
The display scales in Bootstrap generally use the min-width condition and come as follows:
Extra small – widths under 576px –This screen actually doesn't have a media query but the styling for it rather gets applied as a common rules getting overwritten by the queries for the widths above. What's also new in Bootstrap 4 alpha 6 is it actually doesn't use any size infix – so the column layout classes for this screen size get defined like col-6 - such element for example will span half width no matter the viewport.
Extra small-- sizes less than 576px-- This display in fact does not come with a media query but the styling for it instead gets applied as a standard rules getting overwritten by queries for the widths above. What is actually as well brand-new inside of Bootstrap 4 alpha 6 is it actually does not operate any kind of dimension infix-- so the column layout classes for this specific screen dimension get determined like col-6 - such element for example will span half size despite of the viewport.
Small screens-- uses @media (min-width: 576px) ... and the -sm- infix. { As an example element having .col-sm-6 class will certainly cover half width on viewports 576px and larger and full width below.
Medium screens-- applies @media (min-width: 768px) ... as well as the -md- infix. For instance element having .col-md-6 class is going to extend half width on viewports 768px and wider and complete width below-- you've possibly got the drill currently.
Large screens - employs @media (min-width: 992px) ... and the -lg- infix.
And as a final point-- extra-large screens - @media (min-width: 1200px) ...-- the infix here is -xl-
Responsive breakpoints
Considering Bootstrap is actually produced to be mobile first, we work with a small number of media queries to generate sensible breakpoints for designs and user interfaces . These types of Bootstrap Breakpoints Grid are normally depended on minimum viewport sizes and also make it possible for us to size up elements as the viewport changes.
Bootstrap mainly utilizes the following media query ranges-- or breakpoints-- in source Sass documents for arrangement, grid system, and elements.
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
// No media query since this is the default in Bootstrap
// Small devices (landscape phones, 576px and up)
@media (min-width: 576px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, 768px and up)
@media (min-width: 768px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, 992px and up)
@media (min-width: 992px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops, 1200px and up)
@media (min-width: 1200px) ...Since we produce source CSS in Sass, all of media queries are provided by means of Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-up(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(lg) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(xl) ...
// Example usage:
@include media-breakpoint-up(sm)
.some-class
display: block;We sometimes operate media queries that work in the various other path (the supplied display screen scale or even more compact):
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
@media (max-width: 575px) ...
// Small devices (landscape phones, less than 768px)
@media (max-width: 767px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, less than 992px)
@media (max-width: 991px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, less than 1200px)
@media (max-width: 1199px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops)
// No media query since the extra-large breakpoint has no upper bound on its widthOnce more, these particular media queries are likewise obtainable via Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-down(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(lg) ...There are additionally media queries and mixins for aim a specific part of display scales utilizing the lowest and highest Bootstrap Breakpoints Default widths.
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
@media (max-width: 575px) ...
// Small devices (landscape phones, 576px and up)
@media (min-width: 576px) and (max-width: 767px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, 768px and up)
@media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 991px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, 992px and up)
@media (min-width: 992px) and (max-width: 1199px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops, 1200px and up)
@media (min-width: 1200px) ...Such media queries are in addition available via Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-only(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(lg) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(xl) ...Similarly, media queries may well span multiple breakpoint widths:
// Example
// Apply styles starting from medium devices and up to extra large devices
@media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1199px) ...
<code/>
The Sass mixin for focus on the similar display scale range would certainly be:
<code>
@include media-breakpoint-between(md, xl) ...Final thoughts
Together with specifying the width of the web page's components the media queries occur throughout the Bootstrap framework basically getting defined by it - ~screen size ~ infixes. Whenever seen in several classes they should be interpreted just like-- whatever this class is doing it is certainly performing it down to the screen size they are pertaining.
Review several video clip information regarding Bootstrap breakpoints:
Linked topics:
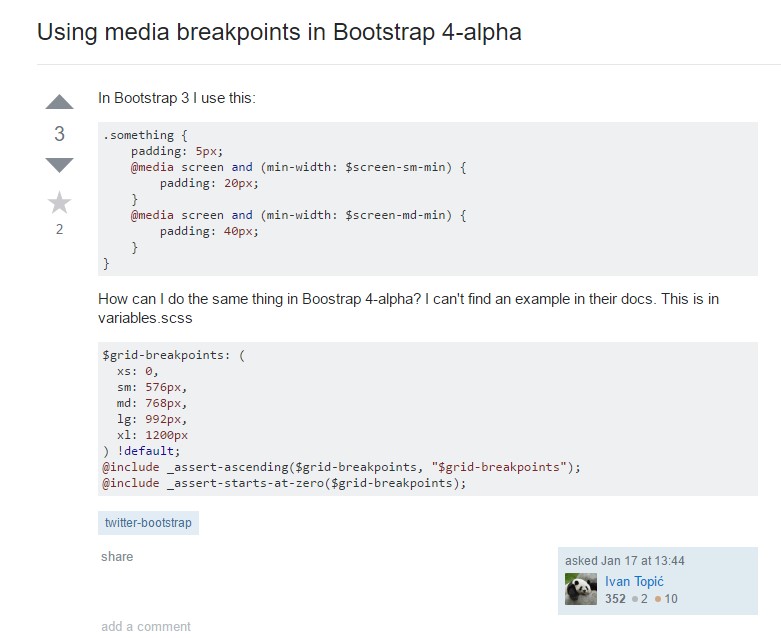
Bootstrap breakpoints formal documents"

Bootstrap Breakpoints complication
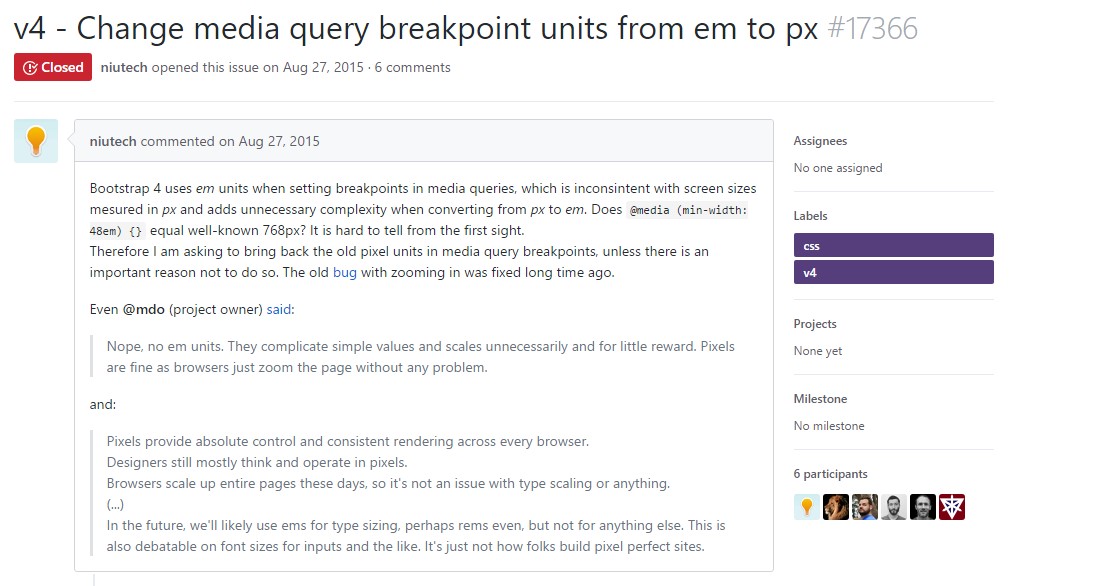
Alter media query breakpoint units from em to px
breakpoints, breakpoints using